.png)
Understanding Thermal Management in Electronics
As electronic devices become increasingly powerful and compact, managing heat effectively is more important than ever. Electronics thermal management refers to the process of controlling the temperature of electronic components to maintain optimal performance, reliability, and safety.
This article provides an overview of thermal management solutions and introduces four commonly used products in this field: cooling fans, heat sinks, thermal pads, and thermal paste.
The Importance of a Thermal Management System
Effective thermal management is crucial for maintaining the smooth and reliable operation of electronic devices. Every electronic component generates heat when in use, and if this heat isn’t properly managed, it can impact performance, reduce lifespan, and lead to reliability issues.
Reduced Performance Due to Thermal Throttling
When excessive heat accumulates, electronic devices often engage in thermal throttling, a protective measure that automatically lowers the device's performance to prevent overheating. While this protects the components from immediate damage, it significantly reduces overall operational efficiency and responsiveness.
Component Degradation and Shortened Lifespan
Continuous exposure to elevated temperatures accelerates the aging process of electronic components. Over time, persistent heat can degrade materials and internal structures, leading to reduced performance and a shortened lifespan. Efficient heat management helps preserve the longevity and reliability of electronic devices.
System Instability and Unexpected Shutdowns
Inadequate thermal management can cause instability within electronic systems, leading to unpredictable behaviour such as sudden shutdowns or operational failures. These unexpected interruptions can negatively impact user experience and productivity, making robust thermal management practices essential for maintaining stable and continuous device operations.
Importance Across Industries
Effective thermal management isn't limited to high-performance computing systems. It's equally vital for everyday consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, which users expect to remain consistently reliable and efficient.
Industrial equipment, which often operates under rigorous conditions and extended periods, also requires robust thermal solutions to sustain optimal performance and prevent operational downtime. Similarly, LED systems, known for their sensitivity to temperature variations, depend on precise heat dissipation to maintain efficiency and longevity. Finally, power electronics, which are central to energy conversion and management systems, generate substantial heat during operation, making effective thermal management indispensable for their safe and reliable operation.
.png)
Key Products in Thermal Management Solutions
Cooling Fans
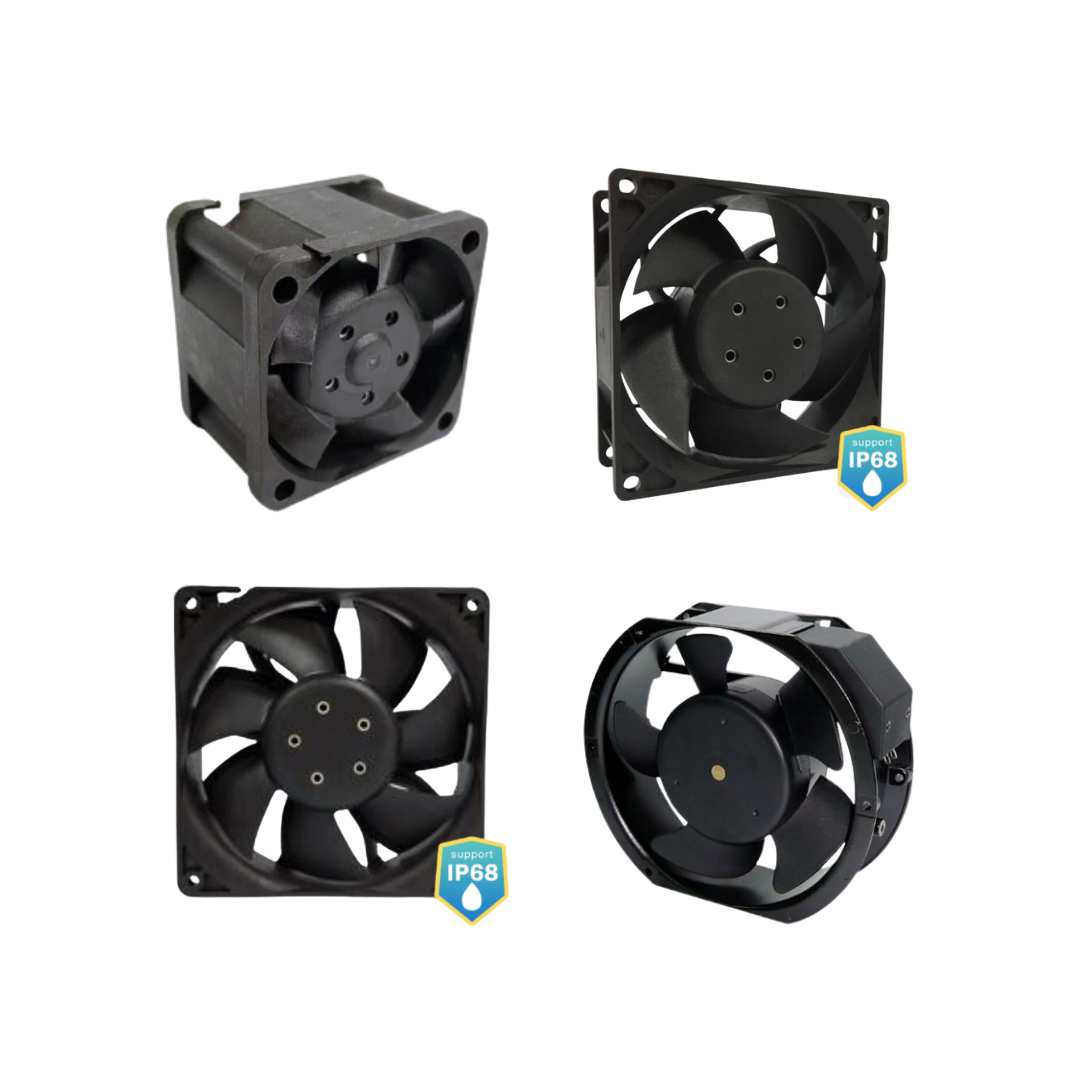

Cooling fans are an active cooling solution designed to move air across components and heat sinks, helping to remove heat and maintain system performance. They are commonly used in desktop computers, power supplies, telecom equipment, and industrial enclosures, anywhere reliable airflow and temperature control are essential.
Types of Cooling Fans:
- AC Fans – Ideal for moving large volumes of air over short distances.
- Centrifugal (Blower) Fans – Deliver higher static pressure, making them ideal for confined or enclosed spaces.
- DC Fans – Energy-efficient and widely used in electronic systems.
When selecting a fan, consider airflow needs, noise level, voltage rating, and size to ensure optimal performance.
At Active Components, we offer a wide selection of dependable cooling fans and provide custom solutions tailored to your application. Contact us today.
Heat Sinks
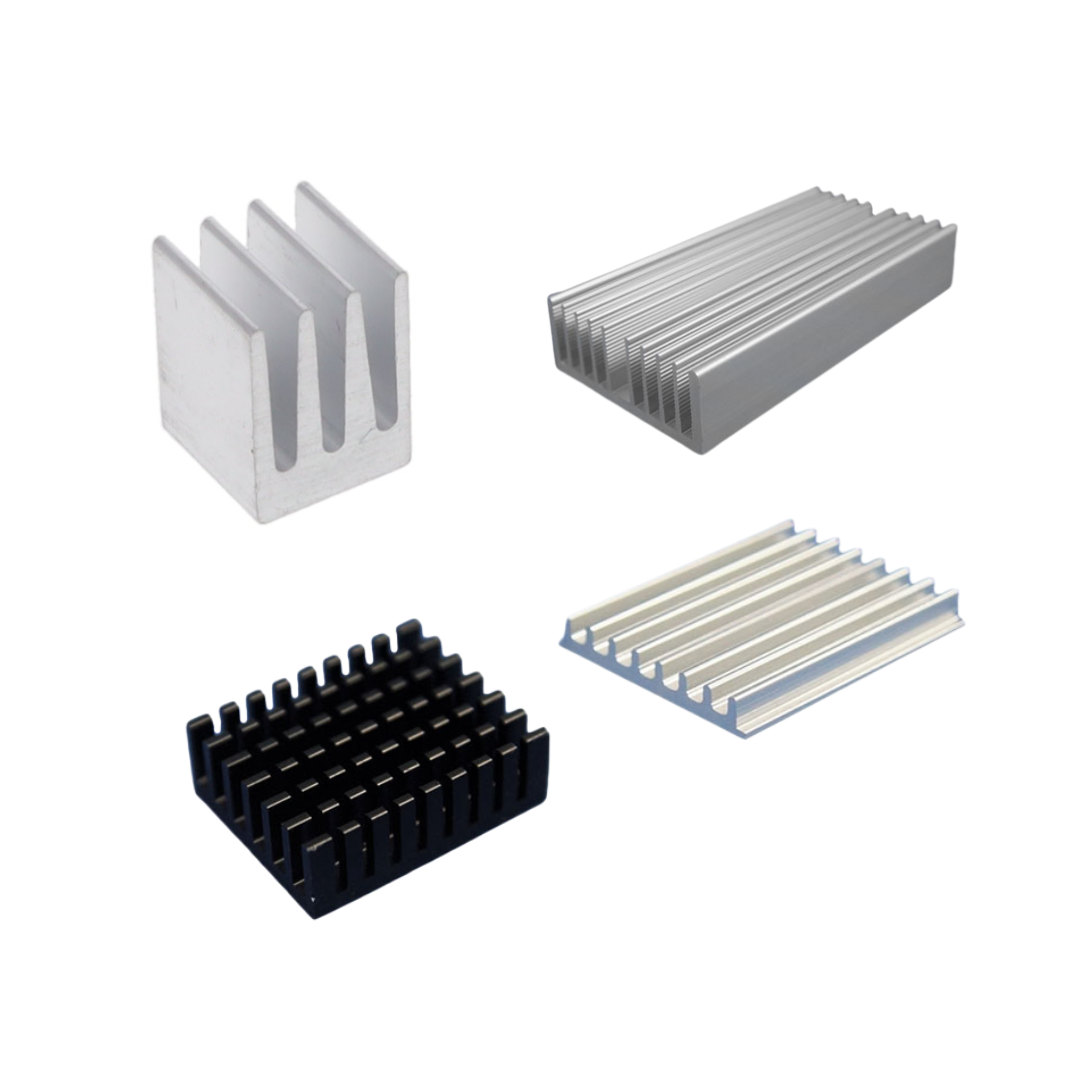

Heat Sinks are passive thermal management components that absorb and dissipate heat from electronic devices. They maintain safe operating temperatures and ensure the performance, reliability, and lifespan of components such as processors, power modules, and LEDs.
A heat sink functions by transferring heat from the surface of a component to the surrounding air. This process begins with conduction, where heat is transferred from the device to the heat sink material, typically aluminium or copper, due to its excellent thermal conductivity. The heat is then released into the air through convection. In natural convection, air flows over the heat sink naturally, while in forced convection, fans or blowers are used to enhance airflow and improve heat dissipation.
Customised Shape
The effectiveness of a heat sink is largely determined by its design, especially the surface area, fin arrangement, and overall shape. A well-designed heat sink allows more heat to escape efficiently, helping to reduce the temperature of the component it protects. Therefore, heat sink geometry should be carefully considered during the design phase of any heat-sensitive application.
In some cases, the metal product enclosure itself may be designed to serve multiple functions, including acting as a heat sink. This approach is particularly effective in compact or sealed systems where space is limited.
At Active Components, we offer professional guidance and support to help you select or customise the proper thermal management solution for your project, whether you require a standalone heat sink or an integrated design within the enclosure.
Thermal Pads
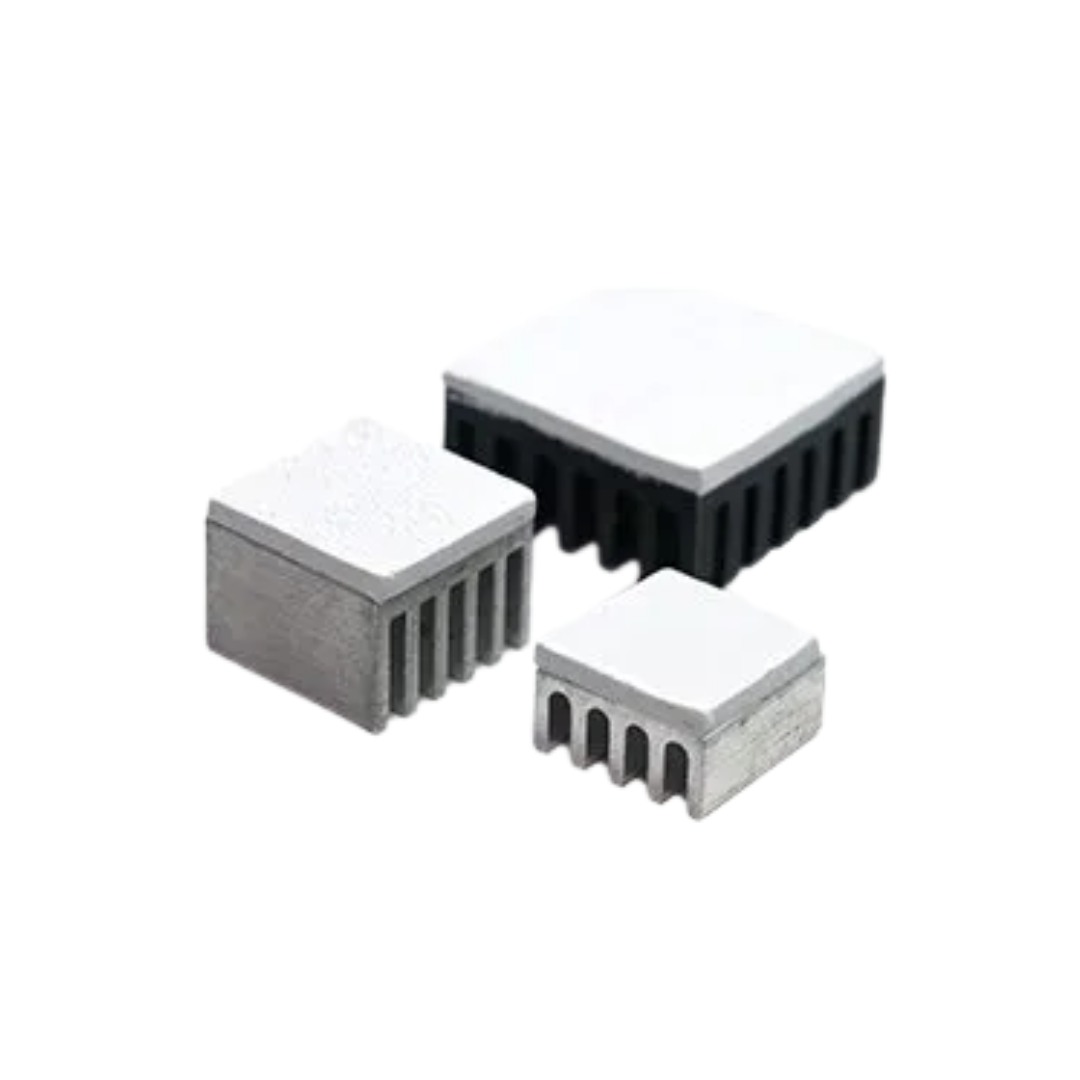 Thermal pads are a type of thermal interface material (TIM) used to enhance heat transfer between heat-generating components and cooling solutions, such as heat sinks or metal enclosures. While components and heat sinks may appear flat, microscopic surface imperfections often create air gaps when they come into contact. These gaps significantly reduce thermal conductivity, as air is a poor conductor of heat.
Thermal pads are a type of thermal interface material (TIM) used to enhance heat transfer between heat-generating components and cooling solutions, such as heat sinks or metal enclosures. While components and heat sinks may appear flat, microscopic surface imperfections often create air gaps when they come into contact. These gaps significantly reduce thermal conductivity, as air is a poor conductor of heat.
Thermal pads address this issue by filling the gaps, ensuring more efficient thermal contact between surfaces. Made from soft, thermally conductive materials, they conform easily to uneven surfaces, allowing heat to move more directly from the component to the cooling medium.
In addition to improving thermal conductivity, thermal pads offer several practical advantages. They are easy to handle and apply, especially compared to thermal pastes, which can be messy or require precise application. Thermal pads also provide consistent thickness and pressure distribution, ensuring uniform thermal performance across the entire surface. Moreover, they are electrically insulating, which protects surrounding circuitry from potential short circuits.
Thermal pads are widely used in graphics cards (GPUs), voltage regulator modules (VRMs), memory modules, and other components that have relatively flat surfaces and require reliable thermal contact. They are particularly well-suited for applications that benefit from ease of assembly or where future rework or replacement may be necessary, such as in prototyping or field servicing.
At Active Components, we supply high-quality thermal pads designed for a wide range of thermal requirements. Whether you're looking for standard sizes or customised shapes and thicknesses, our team can help you select the ideal thermal interface solution to ensure efficient heat transfer and long-term device reliability.
Thermal Paste (Thermal Grease)
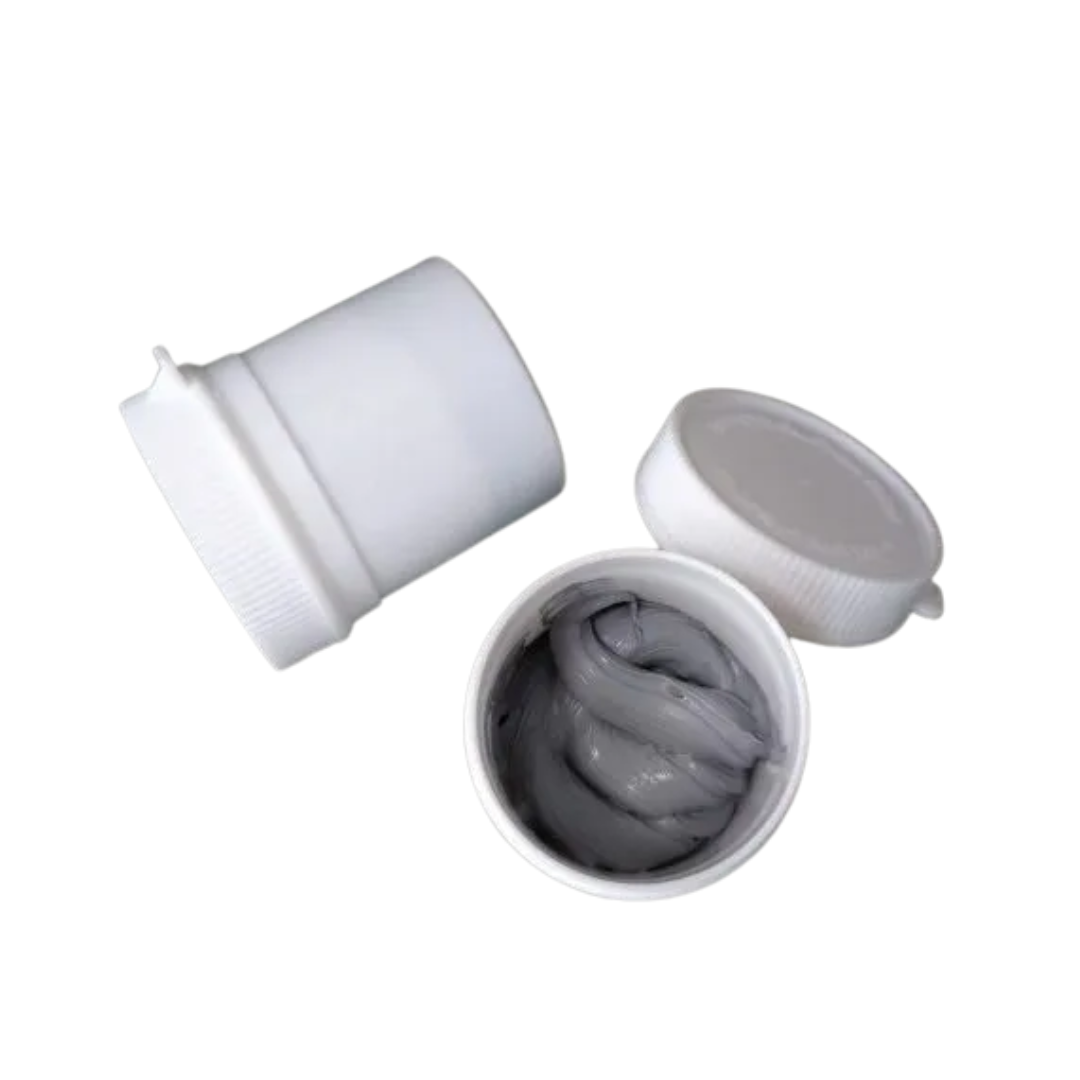

Thermal paste, also known as thermal compound or thermal grease, is a viscous substance used to enhance heat transfer between a processor (or any heat-generating component) and its heat sink. Its primary role is to eliminate microscopic air gaps that naturally occur due to surface imperfections on both the component and the heat sink.
Even when surfaces appear smooth, they contain tiny pits and ridges that trap air when the two surfaces are pressed together. Because air is a poor conductor of heat, these gaps can significantly reduce the efficiency of thermal transfer. Thermal paste fills these voids, creating a more efficient path for heat to transfer from the component to the heat sink.
Thermal paste is composed of thermally conductive particles, such as metal or ceramic, suspended in a polymer-based carrier. These particles increase the paste's ability to transfer heat while the carrier keeps the paste pliable and easy to apply. When a thin, even layer is applied between the processor and heat sink, it spreads under pressure to form a continuous thermal interface that allows heat to flow efficiently.
Compared to thermal pads, thermal paste offers higher thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice in high-performance systems, such as CPUs, GPUs, and other processors, where precise and effective heat management is required.
While thermal paste requires a bit more care during application than thermal pads, it delivers superior thermal performance when applied correctly.
Combining Passive and Active Cooling Solutions
Thermal management includes a wide range of components beyond just fans, heat sinks or Thermal materials. In real-world applications, optimal thermal performance frequently requires a combination of both passive and active cooling strategies:
Passive Cooling Solutions:
These include heat sinks, thermal interface materials, phase-change materials, and thermally conductive enclosures. Passive methods are generally silent, cost-effective, and require minimal maintenance, making them ideal for systems that generate moderate heat.
Active Cooling Solutions:
Active cooling technologies include fans, blowers, heat exchangers, liquid cooling systems, and thermoelectric coolers. These active methods significantly improve heat dissipation, particularly in high-thermal-load scenarios, but introduce additional considerations, such as noise, energy consumption, and maintenance requirements.
By carefully selecting and integrating these thermal management approaches, engineers can ensure that electronic systems consistently operate within safe temperature ranges, thereby effectively balancing performance, cost efficiency, and reliability requirements.
Selecting the Right Thermal Management Solution
The appropriate thermal management strategy must consider several key factors during the design process:
Thermal Load of the System
Determining the thermal load involves calculating the total heat generated by the system's components. Different components, including processors, graphics units, power supplies, and other electronic circuits, produce varying amounts of heat. Accurate assessment of this heat generation is crucial for implementing an efficient cooling solution.
Space Constraints within the Enclosure
The available physical space significantly influences the choice of cooling methods. Compact systems necessitate efficient cooling solutions such as heat pipes, vapour chambers, or micro-channel heat exchangers. In contrast, larger systems may accommodate conventional heat sinks and fan-based cooling arrangements.
Airflow Availability and Direction
Effective airflow management is crucial for efficiently dissipating heat. Evaluating available airflow—including direction, volume, and velocity—helps determine the most suitable component arrangement and cooling solutions. Optimising airflow pathways enhances cooling performance without substantially increasing complexity or cost.
Performance and Cost Trade-offs
Balancing performance and cost is a critical consideration. Advanced cooling methods, such as liquid cooling and sophisticated heat exchangers, provide excellent cooling capabilities but typically come with higher costs. Passive cooling methods, such as heat sinks or thermal interface materials, are more budget-friendly but might be insufficient for systems with high thermal loads.
Have a project with specific thermal management requirements?
Share your specifications with us—our team is here to help you find the right solution. Get in touch today.